Cybersecurity is a part of our Equal Opportunities solutions theme, which focuses on increased access to essential services, such as digital services. Through digital channels, companies and governments provide people with access to digital citizenship: services such as healthcare, education, the justice system, and so on. Cybersecurity is a critical enabler, ensuring that every individual in society has dependable, securely verifiable access to these services, while preserving their privacy.
First, on a basic level, as companies and societies increasingly rely on digital solutions and rates of digitalization grow, all organizations are more vulnerable to cyberthreats, making cybersecurity a growing necessity for them. This driver was already contributing to dependence on secure networks before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, which itself boosted digitalization rates, and in turn the need for cybersecurity. What can we expect in the post-pandemic era? Here’s one indicator that that the effect will be sustained: a new report published by the GSMA [1] and the mobile economy states that dependence on connectivity will remain even after the COVID-19 pandemic. Furthermore, we have moved into a tense new geopolitical climate, following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, creating a growing threat of cyberwarfare. This increases the relevance of cybersecurity solutions, for both government and private sector organizations. The Global Cybersecurity market is expected to grow, from USD 217.9 billion in 2021 to USD 345.4 billion by 2026 [2].
Today, cyberattacks pose a significant threat to businesses of all sizes, government agencies, and individual internet users. In fact, it is the biggest risk factor for business according to Allianz Risk Indicator [3]. And recent cyberattacks have advanced and usually comes from hacktivist groups, lone wolf hackers, and nation-states. Even though it has gotten more common, the first recorded internet attack dates back to 2002. But recent cyberattacks can affect vast numbers of people, meaning that a single attack can usually result in the capturing of data of hundreds of millions of people. Businesses and authorities are now stepping up their strategies to prevent such attacks [4].
Did you know
The first-ever recorded cyberattack happened in 1988. It was the "Morris Worm", a worm program developed by the graduate student Robert Tappan Morris at Cornell University. The Morris Worm could crawl the web to count how many computers were connected to the internet. The program could force computers to crash, and ended up damaging approximately 6000 computers, which at that time comprised 10% of the internet.
Recent well-known cyberattacks and attempts
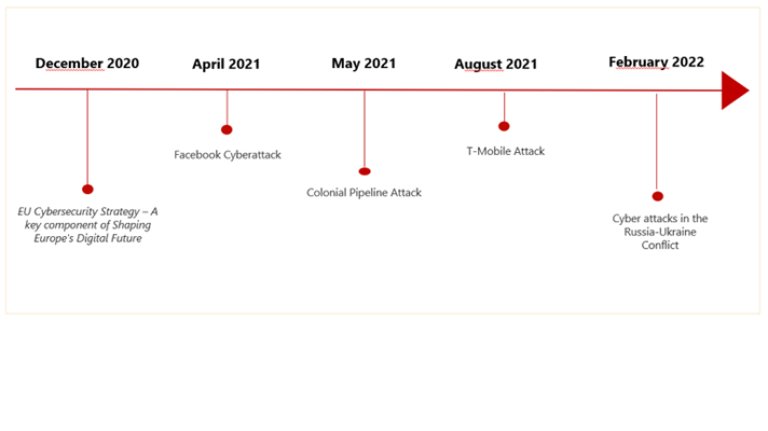
Facebook Cyberattack:
In 2019 hackers obtained information, through scraping, on more than 530 million Facebook users, including their names, Facebook IDs, dates of birth, and relationship status. The information was published online in April 2021.
Colonial Pipeline Attack:
The attack on the Colonial pipeline in May 2021 highlights the increasingly advanced cyberattacks and what type of consequences they can have on people and societies. The attack on a fuel pipeline operator caused fuel disruption and mass panic buying of fuel across the U.S. This also showcases the vulnerability linked to our energy systems.
T-Mobile Attack:
In August 2021, a 21-year-old stole around 106GB of information from T-Mobile customers and prospects. The cybersecurity breach on T-Mobile affected around 50 million existing customers and prospects. The data that was stolen included customer addresses, drivers’ licenses, and social security numbers.
Cyberattacks in the Russia – Ukraine Conflict:
The devastating invasion of Ukraine have displaced and caused many lives. And in addition to the physical battles, cyberattacks are increasingly used in the war. Many sophisticated attacks have happened, including an attack that targeted the State Savings Bank in Ukraine that affected banking services and cash withdrawals [5].
An attempt was also made to shut down Ukraine’s power grid. By targeting one of Ukraine’s largest energy companies, the attack could have caused blackouts affecting millions of people. The attacks are increasing, and the Ukrainian government says the country is experiencing about three times as many hacking attempts as they did before the war began [6].
Cybersecurity companies in our Solutions portfolios The cloud computing model is now widely adopted, due to its powerful and flexible infrastructure. Many organizations are shifting their preference toward cloud solutions, to simplify the storage of data, and because it provides remote server access on the internet, enabling access to unlimited computing power. All three Global Solutions portfolio companies that deliver cybersecurity solutions (Palo Alto, Crowdstrike and Okta) are increasingly focusing on cloud solutions, amongst others.
Palo Alto Networks Inc offers holistic solutions securing protection across network, cloud and mobile users and offers a host of cybersecurity solutions. The company has acquired several cloud products over the past two years and is therefore gaining increases in customer retention and order size. [7]
Crowdstrike specializes in endpoint security and advanced threat detection. All of its solutions are cloud-based and leverage what they call Cloudscale AI which is a technology that continually learns about threats from each recognized attack across their entire client network. Crowdstrike is also expanding into adjacent categories beyond its core focus area of endpoint device security. [8]
Okta specializes in identity management solutions, with a focus on cloud-based systems. The company’s solutions are collaborative, with technology integration and apps more commonly used in business today such as Slack, Zoom, Workday etc.
In addition to the three previously mentioned companies, the Equal Opportunities theme includes KnowBe4, an American company that delivers solutions to prevent human-based errors. Approximately 85% of all cybersecurity breaches involve a human element: KnowBe4 delivers solutions for companies to train their employees on how to avoid making mistakes that can cause cybersecurity breaches. This is an aspect of cybersecurity that is often ignored. [9]
We also see other solutions companies acquiring cybersecurity solutions and companies in order to prevent harmful breaches. For example, IBM recently announced plans to acquire Randori, a leading attack surface manager (ASM) and offensive cybersecurity provider. [10]
The outlook for cybersecurity
With recent and more advanced cyberattacks impacting companies, organizations and governments around the world, there is an increased focus on implementing secure solutions to prevent harmful attacks. As mentioned, cybersecurity has several crossovers, for instance to digital electrical networks, but with the Ukraine invasion, a rising threat of cyberwarfare may ramp up cybersecurity adoption. Consumers, businesses, and nations are monitoring current events and becoming more aware of the increasing threat that cybersecurity has on society. We can expect to see significant investment in cybersecurity products and services, as the cybersecurity market has significant projected growth in the near future.
This article was published in our recently released sustainable investment review for the second quarter of 2022. You can learn more about how we are contributing towards sustainable investments in the new report:
[1] GSMA, ”The Mobile Economy 2022” https://www.gsma.com/mobileeconomy/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/280222-The-Mobile-Economy-2022.pdf
[2] https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/04/05/2416799/0/en/Cybersecurity-Market-Expected-to-Be-Worth-345-4-billion-by-2026-Exclusive-Report-by-MarketsandMarkets.html[3] https://www.allianz.com/content/dam/onemarketing/azcom/Allianz_com/press/document/Allianz_Risk_Barometer_2022_results_APPENDIX.pdf
[4] https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/recent-cyber-attacks
[5] https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/recent-cyber-attacks
[6] https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-61085480
[7] Bloomberg
[8] Bloomberg
[9] https://www.fool.com/investing/2021/09/10/knowbe4-the-cybersecurity-saas-company-youve-never/
[10] https://newsroom.ibm.com/2022-06-06-IBM-Tackles-Growing-Attack-Surface-Risks-with-Plans-to-Acquire-Randori




